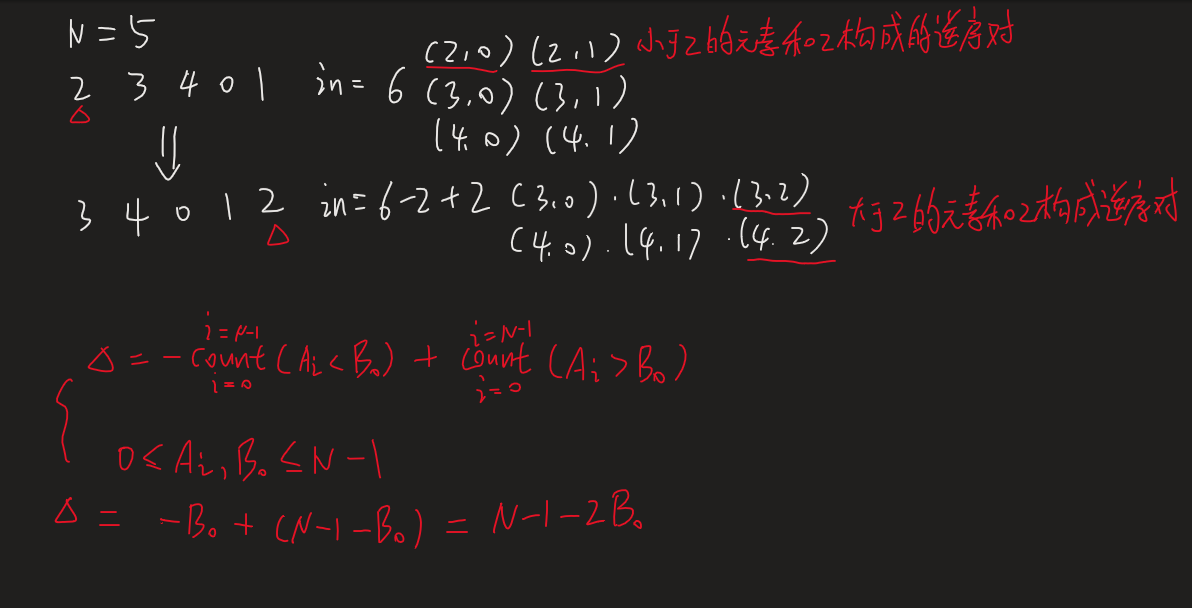比赛地址: https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc190
完整代码(A-F):Github
先下手的人 candies 数量 大于 另一个人就能赢
循环判断
We have
Condition
There are
Constraints
All values in input are integers.
Sample Input 1
4 4 1 2 1 3 2 4 3 4 3 1 2 1 3 2 3
Sample Output 1
解法一 题目大意:有
这个题比赛的时候也卡了一会儿,最后算了下暴力的复杂度,发现直接暴力枚举就行了。枚举所有的放置情况,然后求一个最大值就行了,时间复杂度
import java.util.*;import java.io.*;class Main { static int [] dish; static int [][] w; static int [][] kn; static int K; static int N, M; static int res = 0 ; public static void main (String... args) throws Exception { PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter (new BufferedOutputStream (System.out)); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in)); int [] in = read(br); N = in[0 ]; M = in[1 ]; dish = new int [N]; w = new int [M][2 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < M; i++) { int [] t = read(br); w[i][0 ] = t[0 ]; w[i][1 ] = t[1 ]; } K = read(br)[0 ]; kn = new int [K][2 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < K; i++) { int [] t = read(br); kn[i][0 ] = t[0 ]; kn[i][1 ] = t[1 ]; } dfs(0 ); out.println(res); out.flush(); } public static void dfs (int i) { if (i == K) { res = Math.max(res, check()); return ; } dish[kn[i][0 ]-1 ]++; dfs(i+1 ); dish[kn[i][0 ]-1 ]--; dish[kn[i][1 ]-1 ]++; dfs(i+1 ); dish[kn[i][1 ]-1 ]--; } public static int check () { int cnt = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < M; i++) { if (dish[w[i][0 ]-1 ] >= 1 && dish[w[i][1 ]-1 ] >= 1 ) { cnt++; } } return cnt; } public static int [] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception { return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" " )).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray(); } }
解法二 二进制枚举,赛后独立写出来的,时间复杂度
import java.util.*;import java.io.*;class Main { public static void main (String... args) throws Exception { PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter (new BufferedOutputStream (System.out)); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in)); int [] in = read(br); int N = in[0 ], M = in[1 ]; int [][] cond = new int [M][2 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < M; i++) { int [] t = read(br); cond[i] = new int []{t[0 ]-1 , t[1 ]-1 }; } int K = read(br)[0 ]; int [][] kn = new int [K][2 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < K; i++) { int [] t = read(br); kn[i] = new int []{t[0 ]-1 , t[1 ]-1 }; } int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < (1 <<K); i++) { int [] dish = new int [N]; for (int j = 0 ; j < K; j++) { dish[kn[K-1 -j][(i>>j)&1 ]]++; } int cnt = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < M; j++) { if (dish[cond[j][0 ]] >= 1 && dish[cond[j][1 ]] >= 1 ) { cnt++; } } res = Math.max(res, cnt); } out.println(res); out.flush(); } public static int [] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception { return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" " )).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray(); } }
How many arithmetic progressions consisting of integers with a common difference of
Constraints
Sample Input 1
Sample Output 1
We have four such progressions:
解法一 公差是
import java.util.*;import java.io.*;class Main { public static void main (String... args) throws Exception { PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter (new BufferedOutputStream (System.out)); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in)); long N = Long.valueOf(br.readLine()); long x = 2 *N; HashSet<Long> set = new HashSet <>(); for (long i = 1 ; i*i <= x; i++) { if ((x%i) == 0 ) { set.add(i); set.add(x/i); } } long res = 0 ; for (Long f : set) { if ((x/f+1 -f)%2 ==0 ) res++; } out.println(res); out.flush(); } }
There are
Takahashi is trying to make an ornament by arranging gems in a row.
For some pairs of gems, we can put the two gems next to each other; for other pairs, we cannot. We have
Determine whether it is possible to form a sequence of gems that has one or more gems of each of the kinds
Constraints
All values in input are integers.
If
Sample Input 1
Sample Output 1
解法一 bfs+状态压缩,因为
然后再进行状态压缩,设置状态为: 关键宝石 ,并且以
入口:
转移:
出口:
代码实现如下(注意下标统一,给的输入都是从 1 开始的,需要转换,一开始转换掉了一个,找了半天的 bug):
import java.util.*;import java.io.*;class Main { public static void main (String... args) throws Exception { PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter (new BufferedOutputStream (System.out)); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in)); int [] in = read(br); int N = in[0 ], M = in[1 ]; int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ; List<Integer>[] adj = new ArrayList [N]; for (int i = 0 ; i < M; i++) { int [] t = read(br); int x = t[0 ]-1 , y = t[1 ]-1 ; if (adj[x] == null ) { adj[x] = new ArrayList <>(); } if (adj[y] == null ) { adj[y] = new ArrayList <>(); } adj[x].add(y); adj[y].add(x); } int K = read(br)[0 ]; int [] C = read(br); HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < K; i++) map.put(--C[i], i); int [][] dis = new int [K][K]; Queue<int []> queue = new LinkedList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < K; i++) { Arrays.fill(dis[i], INF); queue.clear(); queue.add(new int []{C[i], 0 }); boolean [] vis = new boolean [N]; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int [] cur = queue.poll(); if (map.containsKey(cur[0 ])) { dis[i][map.get(cur[0 ])] = cur[1 ]; } if (adj[cur[0 ]] == null ) continue ; for (Integer next : adj[cur[0 ]]) { if (vis[next]) continue ; queue.add(new int []{next, cur[1 ]+1 }); vis[next] = true ; } } } int [][] dp = new int [1 <<K][K]; for (int i = 0 ; i < (1 <<K); i++) { Arrays.fill(dp[i], INF); } for (int i = 0 ; i < K; i++) { dp[1 <<i][i] = 1 ; } for (int mask = 0 ; mask < (1 <<K); mask++) { for (int i = 0 ; i < K; i++) { if ((mask&(1 <<i))==0 ) continue ; for (int j = 0 ; j < K; j++) { if ((mask&(1 <<j))==1 || dis[i][j] == INF || dp[mask][i] == INF) continue ; dp[mask|(1 <<j)][j] = Math.min(dp[mask|(1 <<j)][j], dp[mask][i] + dis[i][j]); } } } int res = INF; for (int i = 0 ; i < K; i++) { res = Math.min(res, dp[(1 <<K)-1 ][i]); } if (res == INF) out.println(-1 ); else out.println(res); out.flush(); } public static int [] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception { return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" " )).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray(); } }
Given is a sequence
For each
Constraints
All values in input are integers.
Sample Input 1
Sample Output 1
We have
For
For
For
For
解法一 首先 , ,
import java.util.*;import java.io.*;class Main { static int [] tree; public static int lowbit (int x) { return x & -x; } public static int query (int i) { int res = 0 ; while (i > 0 ) { res += tree[i]; i -= lowbit(i); } return res; } public static void add (int i, int val) { while (i < tree.length) { tree[i] += val; i += lowbit(i); } } public static void main (String... args) throws Exception { PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter (new BufferedOutputStream (System.out)); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in)); int N = read(br)[0 ]; int [] A = read(br); tree = new int [N+1 ]; long res = 0 ; for (int i = N-1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { add(A[i]+1 , 1 ); res += query(A[i]); } out.println(res); for (int i = 0 ; i < N-1 ; i++) { res += N-1 -2 *A[i]; out.println(res); } out.flush(); } public static int [] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception { return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" " )).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray(); } }
一开始写了个假的算法结果 AC 了,主要是离散化写错了(这题本来也不用离散化,写离散化属于我吃饱了撑的,完了还写了个错的,还好,给自己提前暴雷了),幸好我尝试去写了其他的解法,不然这个错误就被混过去了 错误代码 Gist
解法二 进一步的解法,序列的值是完全随机的的做法,这个时候归并就不太行了,而对于树状数组只需要稍微稍微改动一下就行了。
class Main { static int [] tree; public static int lowbit (int x) { return x & -x; } public static int query (int i) { int res = 0 ; while (i > 0 ) { res += tree[i]; i -= lowbit(i); } return res; } public static void add (int i, int val) { while (i < tree.length) { tree[i] += val; i += lowbit(i); } } public static void main (String... args) throws Exception { PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter (new BufferedOutputStream (System.out)); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in)); int N = read(br)[0 ]; int [] A = read(br); tree = new int [N+1 ]; int [][] temp = new int [N][2 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) temp[i] = new int []{A[i], i}; Arrays.sort(temp, (t1, t2)->t1[0 ]-t2[0 ]); int [] rank = new int [N]; for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) { rank[temp[i][1 ]] = i+1 ; } long res = 0 ; for (int i = N-1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { add(rank[i], 1 ); res += query(rank[i]-1 ); } out.println(res); for (int i = 0 ; i < N-1 ; i++) { res -= query(rank[i]-1 ); res += query(N) - query(rank[i]); out.println(res); } out.flush(); } public static int [] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception { return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" " )).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray(); } }
赞赏
感谢鼓励